Goals
- Composition and Data
- Objects in Objects
- Bookkeeping
- Example
- Recursive Objects (sort of)
- Constructor Setup
- Seeding Randomly
- Sampling Area
Resources
Dynamic Programming
Recursive Object Pattern (paper)
"No object is so beautiful that, under certain conditions, it will not look ugly." ~ Oscar Wilde
Objects in Objects
Every time we make an object it has some fields. But what if those fields are other objects. Then there is a much more complex relationship that
must be maintained in your code.
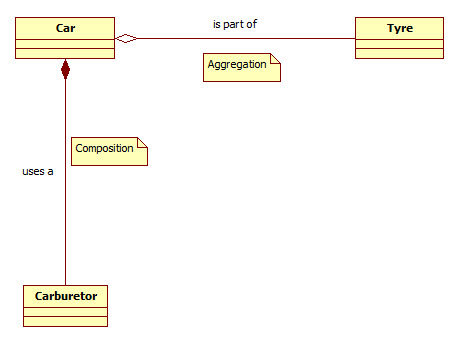
Take for example the car class in the image to the left. Two relationships are shown: aggregation and composition.
Aggregation: the Tyre (or Tire...) has an "is part of" relationship with the Car. Since a Tyre will still be a Tyre if not used specifically as a
field in a Car class.
Composition: the Carburetor on the other hand has an "uses a" relationship with the Car. Since a Carburetor is essentially useless without a Car to
use it, we say that a Car is "composed of" the class Carburetor.
The types and numbers of objects stored within other objects may change, these are basic relationships to think about when designing your classes.
Bookkeeping
It's important to keep all objects up to date. Including those stored inside another object.
A typical scenario is updating a list inside an object. Here's some code from an object that stores and updates a list of positions:
Composition means Object A stores types of Object B and Object B is essentially useless without Object A.
Aggregation means Object A stores types of Object B but Object B can be used on it's own.
Bookkeeping methods update the information inside an object including lists containing other objects.
Recursive Objects - Constructor Setup
Take a look at the following recursive method call:
drawBranch(x, y, px, py, angle - PI/4 * xMouse, step);
Notice that the drawBranch method call has a number of arguments.
Every recursive method has at least 1 parameter. Recursive objects are no different.
We must set up the constructor of an object with parameters that can define a new object in relation to an old one.
Take a look at this constructor:
Segment(float x, float y, float angle, float life) { ... }
When we call new Segment( ... ) we can provide arguments for the location, angle, and life of this new Segment object.
This means that previous Segment objects can now seed new Segment objects with the appropriate values.
Seeding Randomly
It's been talked about before, but making random decisions is a powerful concept:
The basic setup is this:
if ( random(0, 32) < 1) { ... }
Since the random(0, 32) method call returns a float from 0 to 31.99... We have approximately a 1 in 32 chance that the
random number is less than 1, or between 0 and 0.99...
Using this logic, we can decide to seed our recursive objects randomly, and they can also seed objects randomly, and so on.
Why not create new recursive objects all the time? Because we would create so many objects so fast, that it would neither look good
nor would it run properly, crashing our program due to too many objects.
Sampling Area
Somewhat off topic. Say we have an object drawing onto the screen, where other objects are also drawing.
Perhaps we don't want this object to "run over" the other objects already drawn. But there's no information there, only
the pixels that have been colored. What we need to do is sample the pixels and make sure they haven't been drawn yet.
The basic idea is this:
Every recursive definition requires at least 1 parameter.
Seeding must be done randomly and not so fast that too many objects are created.
